Is the Yield Curve Still a Reliable Recession Indicator?
If you’ve been following financial news, you’ve probably heard about the “yield curve” and its reputation as a predictor of recessions. But what exactly is it, and why does it matter? For forex traders and investors, understanding the yield curve is key to anticipating market shifts.
The yield curve displays the interest rates of US government treasuries across different time periods. The yield curve demonstrates that bonds with extended maturities provide higher yields because they expose investors to increased risks throughout their duration. It becomes inverted when short-term interest rates exceed long-term interest rates. It’s inversion throughout history has functioned as an indicator which signals upcoming recessions.
The yield curve maintains its inverted shape during May 2025. The 2-year Treasury yield stands at 3.98% but the 10-year yield reaches 4.37% which produces a -0.39% difference between them. The yield curve inversion has persisted for more than 20 months which marks the longest duration since the early 1980s.
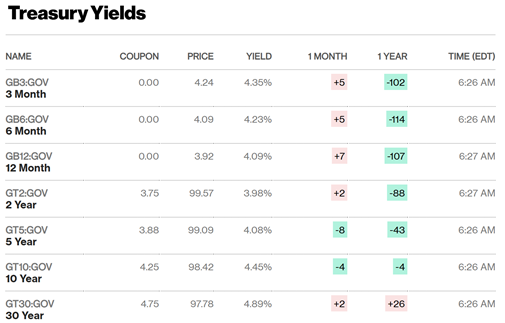
Source: Bloomberg.com. Data as of 13 May 2025.
Economic Indicators: A Mixed Bag
Despite the ominous signal from the yield curve, other economic indicators present a more nuanced picture.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The US economy experienced its first quarterly decline since early 2022 when it contracted by 0.3% during Q1 2025. The trade deficit reached its highest level because imports increased before new tariffs took effect.
- Unemployment Rate: With the overall job market showing resilience at 4.2%, the youth unemployment rate (16 to 19 years old) at 12.9% (almost triple the current unemployment rate) tells a different story. It implies that young workers are finding it difficult to break into the workforce, often the first to be impacted during uncertain times. This crack could be an early red flag, hinting at deeper vulnerabilities in the economy that broader figures might be masking.
- Inflation: The recent implementation of tariffs has caused consumer prices to increase. The April CPI showed a 0.2% increase while core CPI (excluding food and energy) rose by 0.3%. The headline CPI shows a 2.4% year-over-year increase, but core CPI has reached 2.8%.
- Consumer Confidence: The University of Michigan’s Consumer Sentiment Index decreased to 52.2 in April 2025 after reaching 57 in March. The economic uncertainty and inflation worries among consumers led to this decline in sentiment.
Tariffs and Their Economic Impact
The economic environment has become more complex because of recent trade policies. The US government started imposing tariffs on multiple imported goods during the first months of 2025 by placing a 30% duty on Chinese imports. The implemented trade measures have caused consumer prices to increase mainly in the household furnishings sector.
The protection of domestic industries through tariffs creates potential risks for consumer spending and business investment. The Federal Reserve recognizes that trade policies will extend the path toward price stability.
Federal Reserve’s Stance
The Fed has kept its benchmark interest rate at 4.3% for the third straight meeting as it tries to address both inflation and economic growth concerns. Chairman Jerome Powell said that any future rate decisions will be data dependent.
Conclusion: Proceed with Caution
The extended yield curve inversion indicates that a recession is approaching although its presence remains unclear at present. The economy shows strong performance in some areas, yet multiple signs indicate potential weaknesses.
Investors together with policymakers need to track these developments because they are crucial for their decision-making process. The uncertain economic landscape requires investors to diversify their portfolios while maintaining liquidity and staying informed.
Remember, while the yield curve is a valuable tool, it’s one of many indicators. A comprehensive view of the economic landscape is crucial for making informed decisions.